Easy Violin Harmonics Explained!
/Harmonics on the violin often seem over-complicated and confusing, but harmonics on the violin are actually some of the easiest notes to play on the violin! Not only are they easy to play, they’re easy to recognize in music. After you go through this easy guide to violin harmonics I think you will find these special notes on the violin not only easy, but fun to play!
Here’s some common questions about violin harmonics that we’ll cover in this easy guide to harmonics. (Skip ahead if you like).
What are violin harmonics?
What are the different types of harmonics?
What’s the difference between natural and artificial harmonics on the violin?
What are the most common harmonics on the violin?
What Are Violin Harmonics?
The definition of a harmonic is: a wave whose frequency is multiple of the frequency of the same reference wave.
Got it? Okay, good. Moving on.
Just kidding. You don’t need to know anything about waves, overtones, nodes, frequencies, etc to understand violin harmonics.
What is my definition of a harmonic? A note that is played by lightly touching the finger to a particular place on the violin string, which produces a whistling sound.
When you are playing a harmonic, you are touching the string so lightly that you are actually allowing both parts of the string to vibrate (the parts of the string to the left and right of your finger). Think about it. When you put a finger down on the violin fingerboard normally, you’re allowing the string in between the finger and the bridge to vibrate, but the part of the string in between your finger and the nut of the violin doesn’t vibrate.
Allowing both sides of the string to vibrate is one of the things that gives a harmonic its characteristic whistling sound.
How to Play Harmonics on the Violin
Look at your string from the nut (the grooved part at the bottom of the peg box where the strings are touching) to the bridge. Do you see that distance between the nut and the bridge? On a full size violin that’s about 13 inches. You can either measure or just eyeball it, but lightly touch your finger to the string at the mid-point of the string. I do this with my fourth finger but you can do it with any finger. Move your finger around until the harmonic speaks.
Tada! You’ve found the most common harmonic on the violin. The harmonic will occur on the same place on every single string.
What you are playing is a natural harmonic on the violin. It occurs when you divide the string in half. That ration of 2:1 is the simplest ratio you can get, so the harmonic produced there is going to be really easy to play.
There are other natural harmonics on the violin. For instance, if you divide your string length into thirds, you’ll find there’s a natural harmonic right where your 3rd finger would go in first position. (Ever wonder why that finger is a “ring tone” on your violin that really rings when it’s in tune? Now you know).
There’s also a natural harmonic where the fourth finger goes in first position. Just try lightly touching the string and scoot your finger all the way up the fingerboard. You’ll hear lots of natural harmonics. The ones that sound clearly are more simpler ratios. The harmonics that don’t speak so easily are more complicated ratios like 7:1.
What Are the Different Types of Harmonics on the Violin
There’s only two types of harmonics on the violin: natural harmonics (what you just played) and artificial harmonics.
What's the Difference Between Natural and Artificial Harmonics?
Natural harmonics occur when you lightly place your finger on the string. On a full size violin the length of the string from the nut to the bridge is about 13 inches. So you’ll find natural harmonics at certain places, like 6.5 inches up from the nut (the exact middle of the string) Or 4.3 inches up from the nut (the string divided into thirds).
Well those same ratios exist even when playing on a different length of string.
Let’s say we put our first finger down firmly on the first finger in first position. Guess what?! You’ve changed the string length! You’re no longer dealing with a 13 inch string. You’re dealing with something more like a 12 inch string. That means those harmonics that occur when you divide the string in 2 or divide by 3 are going to occur at different places.
So if you keep your first finger down and lightly touch the 4th finger with your pinky, you’re essentially dividing that string into thirds. That’s an artificial harmonic!
An artificial harmonic occurs on the violin when you create an artificial “nut” by placing the first finger firmly down on the string and then placing another finger lightly on the same string to divide the string into thirds and play a harmonic.
How Are Harmonics Notated on the Violin?
There are four ways to notate natural harmonics on the violin. The first two are the most common, but you’ll occasionally see the second two.
The most common natural harmonics are usually notated with a 4 and a 0 or circle. You’ll find this notation for that common natural harmonic that occurs right in the middle of the string.
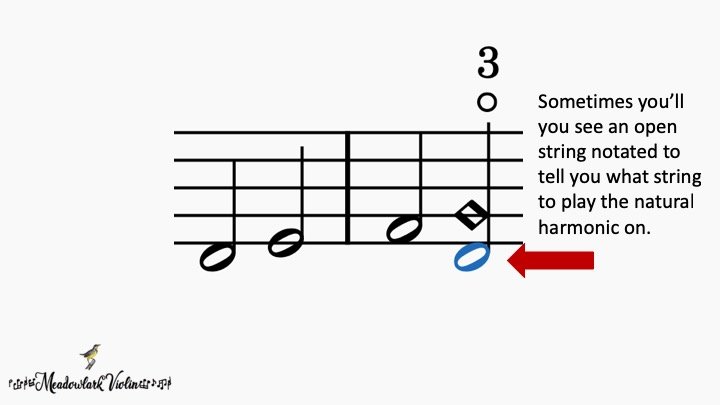
For the other natural harmonics, it’s common to see the note head in an open diamond shape. Sometimes you will also get a number like 3 and a 0 to indicate that note is a harmonic.
Sometimes you will see an open string below a diamond shaped note. The lower string is telling you what string to play this harmonic on. In the example below, you would lightly place your 3rd finger on the “G” note on the D string.
What Are the Most Common Harmonics on the Violin?
These are the most common natural harmonics on the violin. You can play them with third finger in first position, 4th finger in 1st position, or 4th finger in 4th position.
How Are Artificial Harmonics Notated?
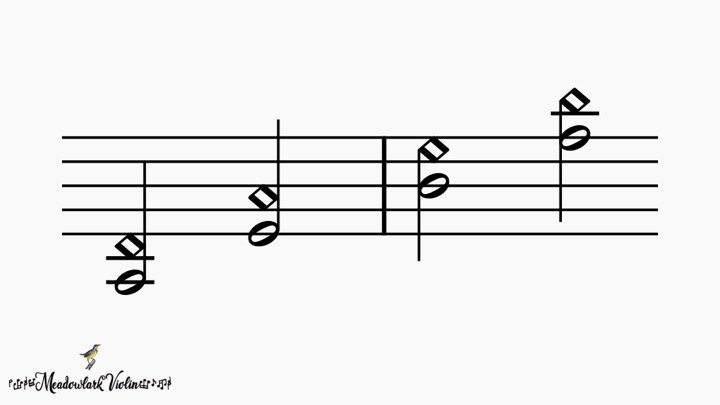
Artificial harmonics often look like a double stop (two notes at once). But the bottom note will look like a normal note and the note on top will be diamond shaped. This is telling you to firmly place the bottom note wherever you would normally place it if it were just by itself. Now lightly place your pinky on whatever note the diamond shaped note is indicating (always on the same string).
Sometimes artificial harmonics look like this.
That’s really all you need to know to be able to identify harmonics in music. Sometimes you’ll see the word harm. to indicate the notes are harmonics. Sometimes you’ll see the word flag. which is short for flageolet, another word for harmonics. But that is somewhat rare.
What's the Most Confusing Way to Write Harmonics?
Wait, you mean you’re not confused? You’re disappointed because you thought harmonics would be sooo much more complicated? Alright, alright. Let me try and confuse you with this form of harmonic notation that you’ll rarely see in most violin music.
So what in the world is this trying to tell us? Are these artificial harmonics or natural harmonics? They’re natural harmonics trying to masquerade as some unnatural aberration.
Sorry natural harmonics, you’re just not that confusing.
Okay, stay with me here. The bottom note tells you what open string to play the harmonic on. The diamond shaped note tells you where to lightly place your finger. And the note in parentheses tells you what pitch is actually sounding.
The diamond note is the only important note in my opinion. The other two notes are completely unnecessary. The bottom note is not needed because where else would you play those diamond shaped notes? How about that first one? Do you want to try and play that G on the E string? Hmmm….probably not a good idea. Why don’t you just play it where you would always play that note! On the D string!
What about the second example? Where else are you going to play that low B? Well there’s only one string you can play that harmonic on, the G string, so your options are kind of limited.
How about those top notes in parentheses? Those are the pitches you are actually producing when you play that natural harmonic. The good news about natural harmonics is that if your finger is in the right place, the harmonic is in tune! No need to get out your tuner to see if that natural harmonic on the D string with 3rd finger is actually indicating that high D.
Composers have already done all the hard work to figure out what pitch they want to sound at that particular place in music. So the parenthetical notes are way more information than you need and often left out of most violin music.
I hope you enjoyed this easy guide to violin harmonics! If you would like more music theory, check out my course on Music Theory that covers pretty much every topic imaginable!
Happy Practicing!
~Lora